Cybereason Security Services issues Threat Analysis reports to inform on impacting threats. The Threat Analysis reports investigate these threats and provide practical recommendations for protecting against them.
In this Threat Analysis report, Cybereason Security Services investigate the Phorpiex botnet which is then able to deliver LockBit Black Ransomware (aka LockBit 3.0).
KEY POINTS
- Automated Executions: Unlike the past LockBit ransomware incidents, the threat actors relied on Phorpiex to deliver and execute LockBit ransomware. This technique is unique as ransomware deployment usually consists of human operators conducting the attack.
- Minimal Change: After the developers of Phorpiex sold the source code of the botnet back in 2021, the successors have likely not changed much of the code base of the malware. This is evident from consistent attempts in deleting Zone.Identifier files throughout different Phorpiex downloader variants.
- Straight To The Point: LockBit downloader variant of Phorpiex downloaded LockBit right away without expanding the infection area within the victim's network. This methodology is different from the usual ransomware operator’s tactics to encrypt as many machines as possible to impact the victim’s network.
INTRODUCTION
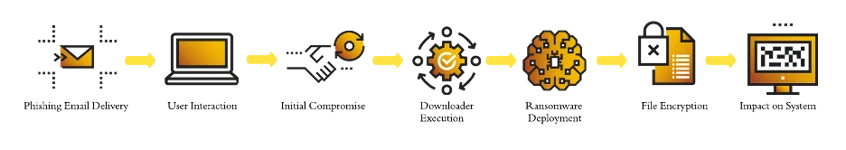
Phorpiex to LockBit Execution FlowChart
What is Phorpiex
Phorpiex, also known as Trik, is a notorious botnet that has been active since 2010, primarily involved in spam campaigns, cryptocurrency mining, and the distribution of post-exploitation malware.
Phorpiex’s adaptability and extensive reach has impacted numerous systems globally through its multifaceted malicious activities. Phorpiex often spreads through attachment or links in phishing emails. The common file types of malicious attachments are Microsoft Word documents, PDFs, or executables. Threat actors behind Phorpiex also abuse compromised websites to host the malware.
What is LockBit
LockBit Ransomware group is a Russian-speaking cybercrime group that emerged around September 2019. At its peak in 2023, Lockbit was responsible for almost 30% of all ransomware attacks.
In February 2024, an international law enforcement effort called Operation Cronos, attempted to dismantle the LockBit ransomware group. Despite several arrests, indictment and revelation of the group’s alleged leader, and disruption of infrastructure, Lockbit returned to operations in short order and remains a significant threat.
The group is known for the following attributes:
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): LockBit operates on an affiliate model, where the group acts as part of the distributor and collects the percentage of the ransom from the affiliates.
Fast Encryption: LockBit advertised to have a rapid encryption process, which minimizes the time available for detection and response.
Wide Target: LockBit targeted various industries such as Logistics, Retail, Consumer Services, Technology, Transportation, Legal, Finance, Construction, Manufacturing, Wholesales, Aviation, Energy, Defense, and Professional Services across multiple regions.
Double Extortion: LockBit often exfiltrates data before encryption systems, threatening to release the stolen data publicly if the ransom is not paid.
Phorpiex to LockBit Connection
The connection between Phorpiex and LockBit primarily lies in the distribution channels and evolution of attack strategies:
Distribution of LockBit: There have been instances where Phorpiex has been used to distribute LockBit ransomware. The botnet’s extensive reach and capabilities make it an effective distribution mechanism for ransomware.
Evolution of Threat Actors: Cybercriminals often evolve their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). Operators behind LockBit leveraged Phorpiex in their existing infrastructure to distribute more lucrative ransomware.
Wide Target: LockBit targeted various industries such as Logistics, Retail, Consumer Services, Technology, Transportation, Legal, Finance, Construction, Manufacturing, Wholesales, Aviation, Energy, Defense, and Professional Services across multiple regions.
Botnet as a Service: The operators behind Phorpiex might offer their botnet infrastructure as a service to other cybercriminals, including those spreading LockBit.
TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
This section covers the technical analysis of Phorpiex downloaders. The analysis consists of two sections:
- TTPs
- Phorpiex Binary Analysis
Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)
In this campaign, not only did Cybereason observe the LockBit downloader version of Phorpiex, but also the TWIZT downloader version of Phorpiex. This section highlights key TTPs seen in both variants.
 LockBit Infection Flow
LockBit Infection Flow
 TWIZT Infection Flow
TWIZT Infection Flow
Phishing Email
Phorpiex infection flow begins with phishing emails with the subject Your Document. The emails with ZIP files named document.zip were sent from jenny@gsd[.]com and ebe6941ee8a10c14dc933ae37a0f43fc@gsd[.]com. The email appears to be responsible for delivering both the LockBit downloader version of Phorpiex or TWIZT downloader variant.
 Phishing Email From gsd[.]com Observed In Cybereason XDR Platform
Phishing Email From gsd[.]com Observed In Cybereason XDR Platform
 Emails Subject, Senders And Attachment Zip Files
Emails Subject, Senders And Attachment Zip Files
For each variant, the file consisting within the ZIP file differs.
- SCR file:LockBit variant
- LNK file: TWIZT variant
LNK File
TWIZT variant delivers LNK file document.doc.lnk within the attached ZIP file document.zip. The LNK file is responsible for downloading spl.exe from hxxp://twizt[.]net and saving it as windrv.exe on the victim's machine under %userprofile% folder.
 Shortcut File Leads PowerShell Execution
Shortcut File Leads PowerShell Execution
Windrv.exe appears to be TWIZT downloader variant, which this report dives into more details later.
SCR File
 Malicious SCR file Detection By Cybereason
Malicious SCR file Detection By Cybereason
LockBit downloader variant delivers SCR file pic0502024.jpg.scr within the ZIP file document.zip. When the victim executes the SCR file, it creates a connection to IP address 193.233.132[.]177. At the time of this execution, Cybereason did not observe a successful connection to 193.233.132[.]177, however according to ProofPoint's blog, the IP address hosted LockBit ransomware.
 Connection To IP Address 193.233.132[.]177
Connection To IP Address 193.233.132[.]177
The process PIC0502024.jpg.scr attempts to download LockBit binary lbbb.exe from IP address 193.233.132[.]177 and renames it with a random generated SCR file name in folder %TEMP%.
 GET Request To Download lbbb.exe
GET Request To Download lbbb.exe
Phorpiex Binary Analysis
This section covers binary analysis of three different Phorpiex variants:
LockBit Downloader
GandCrab Downloader
Phorpiex TWIZT Downloader
Analysis samples consist of following Secure Hash Algorithm 256 (SHA-256) signatures:
|
Filename
|
SHA-256
|
Description
|
|
PIC0502024.jpg.scr
|
263a597dc2155f65423edcee57ac56eb7229bdf56109915f7cb52c8120d03efb
|
LockBit downloader variant
|
|
DeviceManager.exe
|
5a1ab27b99f3fe6cbe825f2743c77347a7339783f8a22d99a54be2d07b94c1a8
|
GandCrab downloader variant
|
|
windrv.exe
|
c2dcdab49f620d41cdff93c58a50c760906ea2565001145564a1491defec08f4
|
Phorpiex TWIZT Downloader
|
Cybereason added a GandCrab downloader variant analysis to give additional insights for the comparative analysis.
LockBit Downloader Variant
URL Cache Deletion
Before initiating download of the LockBit ransomware, the downloader deletes the URL cache of the C2 hxxp://193.233.132[.]177/lbbb.exe via DeleteUrlCacheEntryW. The downloader utilizes this methodology to likely prevent broken cache from hindering the downloading process.
 Deletes URL Cache Via DeleteUrlCacheEntryW
Deletes URL Cache Via DeleteUrlCacheEntryW
Library Obfuscation
As part of its anti-analysis capabilities, the LockBit Downloader variant employs encrypted strings as part of code obfuscation. This variant includes a decryptor function responsible for revealing these strings.
 Decryptor Function Code Snippet
Decryptor Function Code Snippet
Many of these encrypted strings are library names and function names, which are dynamically loaded by the downloader during the runtime. The decryptor function returns the decrypted strings that are then passed into either LoadLibraryA or GetProcAddress to load necessary libraries.
 Decrypting Library Name wininet.dll And Loading The Library Via LoadLibraryA
Decrypting Library Name wininet.dll And Loading The Library Via LoadLibraryA
LockBit Download & Execution
Once necessary executions complete, the downloader attempts to download LockBit binary lbbb.exe from the C2 server. The downloading process consists of:
- Fetching full directory path of %temp%
- Creating a new SCR file name with randomly generated numbers
- Creating a full file directory combining 1. and 2.
- Downloading lbbb.exe file from C2 hxxp://193.233.132[.]177
- Writing lbbb.exe onto the full directory path mentioned in Step 3
 Code Snippet Of LockBit Download
Code Snippet Of LockBit Download
Once the downloader process finishes, it attempts to execute LockBit via ShellExecuteA.
Indicator Removal
The downloader ensures to delete the Zone.Identifier file in order to hide the trace and evidence of C2 metadata. The Zone.Identifier file is responsible for storing metadata on downloaded files such as the URL hosting the downloaded files.
 Zone.Identifier Content Example
Zone.Identifier Content Example
Since Zone.Identifiers often consist of the host URL of the downloaded files, the downloader attempts to delete all of Zone.Identifiers related to Phorpiex variants.
 Deletes Zone.Identifier File Of The Downloaded LockBit
Deletes Zone.Identifier File Of The Downloaded LockBit
Phorpiex TWIZT Downloader Variant
JPEG File Check
After the TWIZT variant LNK file downloads the binary payload from C2, the binary creates an empty JPEG file under the %TEMP% folder. The process windrv.exe confirms the presence of the JPEG file in %TEMP% folder. This procedure verifies the machine is a new host to avoid re-infecting it.
 Confirm Existence Of The JPEG File
Confirm Existence Of The JPEG File
 Create The JPEG File In %TEMP% Folder
Create The JPEG File In %TEMP% Folder
 Connect To twizt[.]net/installed
Connect To twizt[.]net/installed
If the JPEG file does not exist, the downloader connects to twizt[.]net/Installed, which likely notifies C2 of the new victim host.
Mutex Creation
As part of checking the mechanism of the infection status within the victim’s machine, the downloader creates a mutex named PreLoad via CreateMutexA after the JPEG file check. If PreLoad mutex already exists within the machine, the process exits.
 Mutex PreLoad Creation
Mutex PreLoad Creation
Indicator Removal
The TWIZT downloader ensures to remove evidence and trace of the downloaded files by deleting Zone.Identifier file, same as LockBit downloader.
Persistence Via Registry Run Key
To maintain persistence within the victim’s machine, the downloader conducts following actions:
- Fetches full directory path of %userprofile%
- Copies and renames itself as %userprofile%\winsvc.exe
- Register renamed file winsvc.exe as Windows Service in the registry run key.
 Copies Itself Into %userprofile% Via CopyFileW
Copies Itself Into %userprofile% Via CopyFileW
 Creates Persistence By Registering Copied File Via Registry Run Keys
Creates Persistence By Registering Copied File Via Registry Run Keys
 Registry Manipulation To Execute Automatically
Registry Manipulation To Execute Automatically
Payload Download & Execution
After necessary executions complete, the downloader attempts to retrieve the actual payload from the C2 server. The downloading process consists of:
- Fetching full directory path of %temp%
- Creating a new file name with randomly generated numbers.
- Creating a full file directory combining 1. and 2.
- Downloading lslut.exe file from C2 hxxp://twizt[.]net
- Writing lslut.exe onto the full directory path mentioned in Step 3.
 Code Snippet Of Payload Download
Code Snippet Of Payload Download
Once the download finishes, the downloader attempts to delete the Zone.Identifier file and execute the newly downloaded file via CreateProcessW or ShellExecuteW.
 Code Snippet Of Process Creation Of lslut.exe
Code Snippet Of Process Creation Of lslut.exe
GandCrab Downloader Variant
Anti-SandBox
GandCrab Downloader consists of an anti-sandbox feature, which checks the existence of following modules or processes with combinations of CreateToolhelp32Snapshot, Process32First, and Process32Next.
|
Blocklisted Files
|
|
dir_watch.dll
|
|
prl_cc.exe
|
|
prl_tools.exe
|
|
python.exe
|
|
pythonw.exe
|
|
sbiedll.dll
|
|
tpautoconnsvc.exe
|
|
vboxcontrol.exe
|
|
vboxservice.exe
|
|
vboxtray.exe
|
|
vmsrvc.exe
|
|
vmtoolsd.exe
|
If any of the above modules or processes exist within the environment, the process terminates itself with ExitProcess.
Defense Evasion
The downloader updates two registries in order to impair defense of the victim’s machine.
- Disable Windows Defender’s AntiSpyware feature
- Add DisableAntiSpyware in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\
- Register the current process into the AuthorizedApplication list in Firewall Policy for Windows Defender.
- Add current process’ filepath in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SharedAccess\Parameters\FirewallPolicy\StandardProfile\AuthorizedApplications\List\
Execution Flow Obfuscation
GandCrab downloader variant consists of a feature where the binary overwrites the .text section during the runtime as part of code obfuscation. The deobfuscation flow consists of the following steps:
- Fetch and decrypt shellcode, obfuscated header and .text section code from .rsrc section
- Execute decrypted shellcode
- Update memory protection of header and .text section
- Zero out current header and .text section of the downloader process
- Write decrypted header and .text section into the zeroed out sections from 4.
 Memory Protection Update Via VirtualProtect
Memory Protection Update Via VirtualProtect
 .text Section Rewrite
.text Section Rewrite
Indicator Removal
The downloader ensures to remove evidence and trace of the downloaded files by deleting Zone.Identifier file, same as LockBit downloader.
Persistence via Registry Run Key
To maintain persistence within the victim’s machine, the downloader performs the following actions.
- Fetches full directory path of %SystemRoot%
- Creates new directory %SystemRoot%\T-50979593940500600407640
- Copies and renames itself as %SystemRoot%\T-50979593940500600407640\winsvc.exe
This persistence mechanism is similar to the Phorpiex TWIZT downloader variant, the only difference is the directory location.
Comparative Analysis
This section covers the comparative analysis between LockBit Downloader, GandCrab Downloader and Phorpiex TWIZT Downloader variants.
|
Tactics
|
LockBit Downloader
|
Phorpiex TWIZT Downloader
|
GandCrab Downloader
|
|
Anti-Sandbox
|
|
|
✔
|
|
Disable Microsoft Defender AntiVirus via DisableAntiSpyware
|
|
|
✔
|
|
Execution Flow Obfuscation
|
|
|
✔
|
|
JPEG File Check
|
|
✔
|
|
|
Library Obfuscation
|
✔
|
|
|
|
Mutex Creation
|
|
✔
|
|
|
Persistence via Registry Run key
|
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
Register itself into authorized application list
|
|
|
✔
|
|
Removal of Zone.Identifier
|
✔
|
✔
|
✔
|
|
URL Cache Deletion
|
✔
|
|
|
IOCs
|
IOC
|
IOC type
|
Description
|
|
twizt[.]net
|
Domain Name
|
C2 related to TWIZT downloader variant
|
|
193.233.132[.]177
|
IP Address
|
C2 hosting LockBit binary
|
|
a861d931cbeb1541193c8707a7114e21daf4ad6d45099427b99a9d0982d976ae
|
SHA-256
|
ZIP file related to TWIZT downloader variant, delivered via phishing emails.
|
|
05ca9f97a27b675d24edf621b716159ddebff4f16f70b15b2ca68fc7203308b7
|
SHA-256
|
Document.doc.lnk within the attached ZIP file document.zip.
|
|
01cd4320fa28bc47325ccbbce573ed5c5356008ab0dd1f450017e042cb631239
|
SHA-256
|
ZIP file related to LockBit downloader variant, delivered via phishing emails.
|
|
c2dcdab49f620d41cdff93c58a50c760906ea2565001145564a1491defec08f4
|
SHA-256
|
TWIZT downloader executable
|
|
r263a597dc2155f65423edcee57ac56eb7229bdf56109915f7cb52c8120d03efb
|
SHA-256
|
LockBit downloader executable
|
|
5a1ab27b99f3fe6cbe825f2743c77347a7339783f8a22d99a54be2d07b94c1a8
|
SHA-256
|
GandCrab downloader executable
|
Cybereason Recommendations:
Cybereason recommends the following actions in the Cybereason Defense Platform:
- Enable Application Control to block the execution of malicious files.
- Enable Anti-Ransomware in your environment’s policies, set the Anti-Ransomware mode to Prevent, and enable Shadow Copy detection to ensure maximum protection against ransomware.
- Enable Variant Payload Prevention with prevent mode on Cybereason Behavioral execution prevention.
Cybereason is dedicated to teaming with Defenders to end cyber attacks from endpoints to the enterprise to everywhere. Learn more about Cybereason XDR powered by Google Chronicle, check out our Extended Detection and Response (XDR) Toolkit, or schedule a demo today to learn how your organization can benefit from an operation-centric approach to security.
MITRE ATT&CK MAPPING
|
Tactic
|
Techniques / Sub-Techniques
|
Summary
|
|
TA0001: Initial Access
|
T1566.001 - Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment
|
Phorpiex arrives on to the system when a TA sends emails consisting of zip files which contain variants of Phorpiex.
|
|
TA0002: Execution
|
T1204.002 - User Execution: Malicious File
|
When the user executes the malicious files (.lnk, .scr) within those zip files it makes connections to C2 to download additional payload.
|
|
TA0003: Persistence
|
T1547.001 - Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder
|
Phorpiex TWIZT and GandCrab variant manipulates the registry to automatically execute.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1070.009 - Indicator Removal: Clear Persistence
|
Removes traces of downloaded files by deleting zone.identifier.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1562.001 - Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools
|
Phorpiex GandCrab variant observed disabling windows defender’s AntiSpyware feature and registering process into Firewall Policy for Windows Defender.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1027.002 - Obfuscated Files or Information
|
Aim to evade static analysis and make the file appear less suspicious or different from known signatures.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1497.001 - Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: System Checks
|
Phorpiex GandCrab variant checks the modules or processes to detect virtualization and analysis environments.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1497.003 - Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: Time Based Evasion
|
Phorpiex checks system time or uses sleep functions to detect if it is running in a sandbox (where time might be manipulated or slower).
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1036.007 - Masquerading: Double File Extension
|
LockBit downloader variant uses extension .jpg.scr to masquerade the true file type.
|
|
TA0005: Defense Evasion
|
T1036.008 - Masquerading: Masquerade File Type
|
Phorpiex was observed downloading LockBit binary and then renaming it with a random generated SCR file name and saving it in the temp folder to achieve persistence, stealth and evading detection.
|
|
TA0011: Command and Control
|
T1071 - Application Layer Protocol
|
Threat actors communicate with C2 to download additional payloads of LockBit or GandCrab executables.
|
ABOUT THE RESEARCHER
Mahadev Joshi, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC

Mahadev Joshi is a Security Analyst with the Cybereason Global SOC team. He is passionate about cybersecurity and malware analysis, with a focus on understanding and countering advanced threats. He is eager to learn more and stay ahead of emerging threats. Mahadev has a Bachelor of science in Information Technology.
Masakazu Oku, Senior Security Analyst, Cybereason Global SOC

Masakazu Oku is a Security Analyst with the Cybereason Global SOC team.
He works as a SOC analyst and investigates security events on a daily task. He is interested in threat intelligence, malware analysis and APT campaigns. He had a Master's degree in Information Science from Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST).






























