Over the past year, the Cybereason Nocturnus Team has observed various trends among cyber criminals and nation-state groups leveraging various global events such as COVID-19 and other topical themes and trending issues as phishing content to lure their victims into installing their malware of choice.
As the tax season is already here, Cybereason detected a new campaign targeting US taxpayers with documents that purport to contain tax-related content, ultimately delivering NetWire and Remcos - two powerful and popular RATs (remote access trojans) which can allow attackers to take control of the victims’ machines and steal sensitive information.
Key Points
- Leveraging US Tax Season to lure victims: Each year, by April 15th, all US citizens are expected to deliver their tax returns. Cybereason detected a phishing campaign targeting US taxpayers.
- Delivering two types of commodity malware: Two infamous remote access tools (RATs) are being used in this campaign, NetWire and Remcos, each manifesting as binaries delivered via malicious documents.
- Evading heuristic and AV detection mechanisms: The malicious documents that infect the user are roughly 7MB in size, which allows them to evade traditional AV mechanisms and heuristic detection.
- Abuse of legitimate cloud services: The infection chain uses cloud services such as “imgur” to store the Netwire and Remcos payloads, hidden in image files
- Steganography: Payloads are concealed and downloaded within image files, combined with the fact they are hosted on public cloud services makes them even harder to detect.
- Exploiting legitimate OpenVPN clients: As a part of the infection process, a legitimate OpenVPN client is downloaded and executed then sideloads a malicious DLL that drops NetWire/Remcos.
Background
The campaign bears resemblance to another campaign observed in April of 2020 which also delivered the NetWire RAT. Both NetWire and Remcos are commercial RATs that are available for purchase online for rather affordable prices of as little as US$10 per month. Both offer various licensing plans and following the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model, offering their customers a subscription-based model with services such as 24/7 support and software updates:
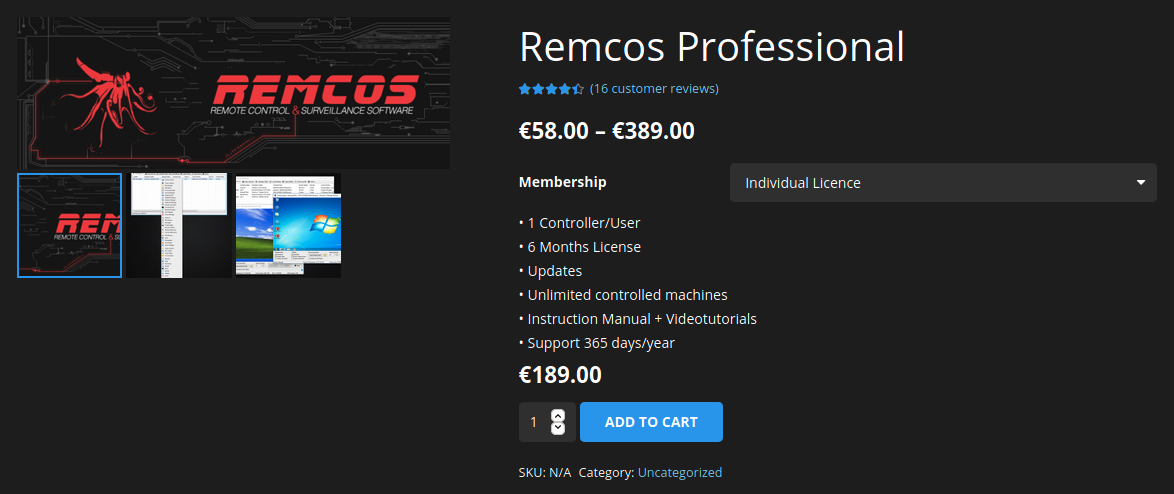
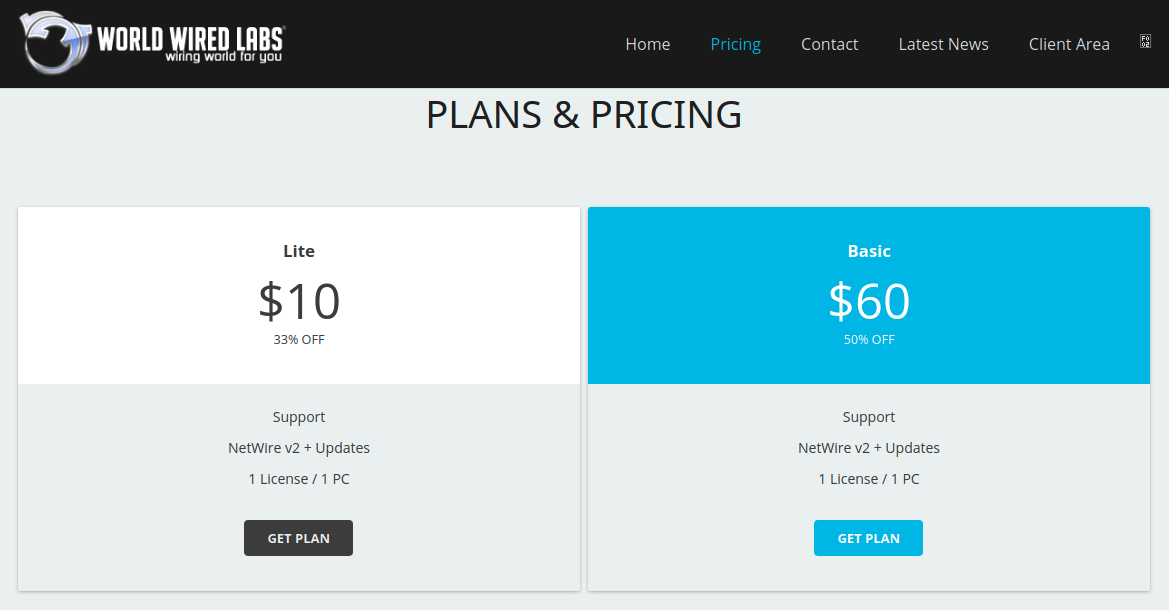 Remcos and NetWire as offered on their websites
Remcos and NetWire as offered on their websites
campaign analysis
Infection Vector: Lure Documents Containing a Malicious Macro
The infection vector that lures the users into installing the malware is a tax return themed Word document containing a malicious macro:
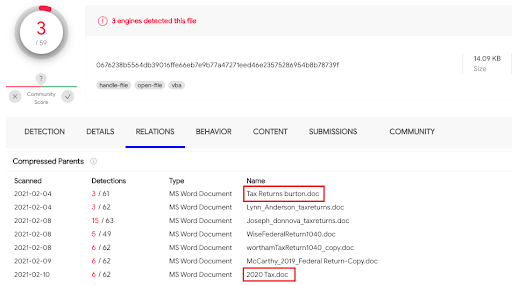 Malicious documents submitted to VirusTotal
Malicious documents submitted to VirusTotal
Once the document has been opened, the content in the background is allegedly blurred, and the “Enable Editing” and “Enable Content” prompts must be manually confirmed by the user:
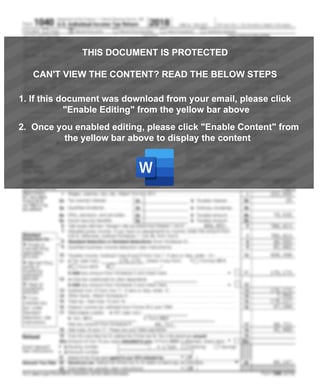

Malicious documents content
This is a known social engineering method used to encourage the user to enable embedded macros to run on their machine. Once the malicious content is being executed, an embedded and heavily obfuscated macro is ran on the victim’s machine:
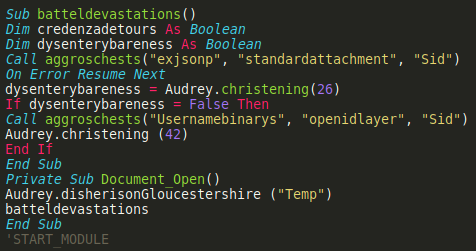 A part of the embedded macro obfuscated code
A part of the embedded macro obfuscated code
The above code partially shows that the payload is eventually dropped in the users “Temp” directory:
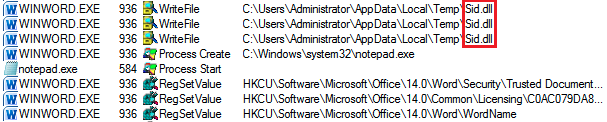 The DLL dropped by the macro code
The DLL dropped by the macro code
Finally, the DLL is injected into notepad and continues the infection chain.
Loaders
The “sid.dll” loader that was dropped by the macro was observed to have at least two different variants: one is a loader for Remcos, and the other is a loader for NetWire. Looking at their exports, both loaders share the same “payload” exported method:
.png?width=512&name=unnamed%20(1).png) The loader’s exported methods
The loader’s exported methods
Upon execution, the “payload” method starts decrypting data using a XOR key:
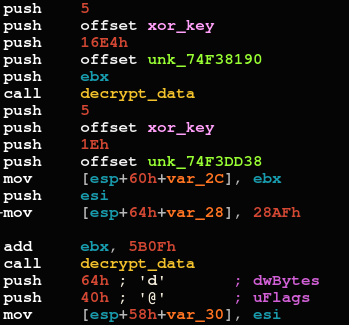 Dat decryption methods of the NetWire loader
Dat decryption methods of the NetWire loader
The first decrypted part is an additional executable code, and the second part is decrypting the URL the loader connects to in order to download the next execution stage:
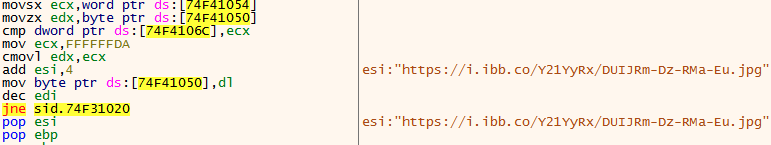 The decrypted initial C2 URL
The decrypted initial C2 URL
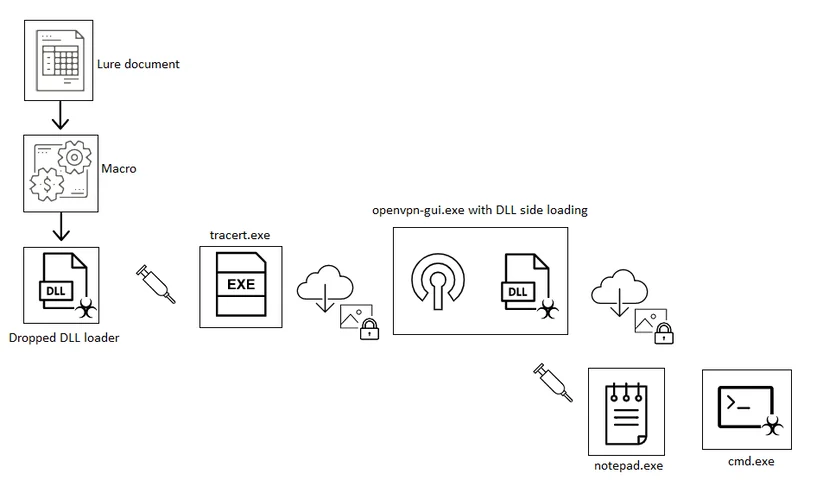
Eventually, the malicious code is injected into “tracert.exe” that downloads the OpenVPN client along with a trojanized DLL file called “libcrypto-1_1.dll”, which will be side-loaded to the OpenVPN client upon execution. A similar process, most likely by the same threat actor, was mentioned earlier this year and describes documents that date back to middle 2020. It then creates a persistence for the VPN client by creating automatic execution of a .lnk file (C:\Users\%username%\AppData\Local\Temp\openvpn-gui.lnk).
OpenVPN DLL Sideloading
The malicious code in the sideloaded DLL unpacks an additional DLL in-memory and injects it into “notepad.exe”. A secondary payload hidden in an image file is then downloaded from “imgur.com”, a well-known cloud image storage service. The decrypted payload can be either NetWire or Remcos:
 Screenshot of an image concealing a malicious payload
Screenshot of an image concealing a malicious payload
Remcos
The features for the Remcos RAT can be found on its official website, and includes:
• Remote execution of shell commands on the infected machine
• Downloading and execution of additional payloads
• Screen capture
• Clipboard data management
The version that is used in this campaign is 3.0.0 professional, which also offers support and software updates:
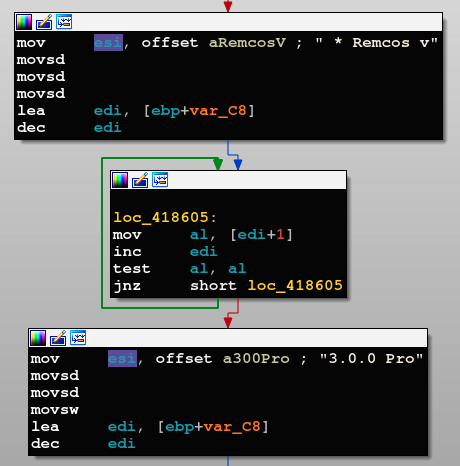 Remcos variant as seen in its code
Remcos variant as seen in its code
netwire
NetWire has been active for years, and in 2019 a new version was spotted in the wild. Some of the most notable features of NetWire include:
• Downloading and execution of additional payloads
• File and system managers
• Screen capture
• Browser credentials and history theft
• Gathering information about the victim’s system
Similar to Remcos, the NetWire malware also contains indicative hardcoded strings:
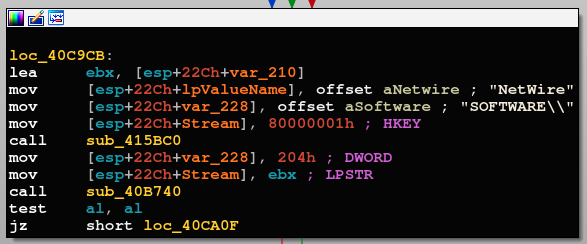
NetWire hardcoded strings
Cybereason Detection and Prevention
The Cybereason Defense Platform detects the execution of a malicious Word document used in the operation:
Once persistence is created in the first stage, the second stage of the attack is also detected, monitoring Remcos/NetWire injected into cmd.exe:
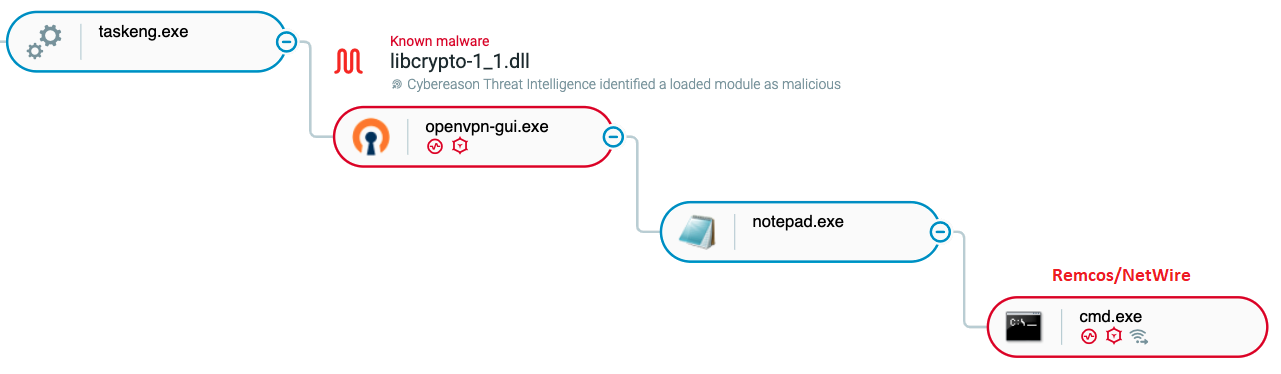
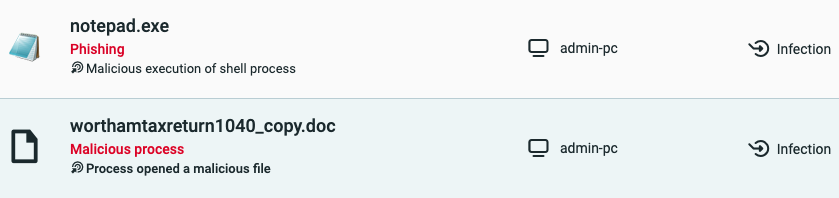
Corresponding Malops(™) are then triggered:
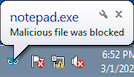
When the malicious sideloaded DLL is loaded by “openvpn-gui” in Prevention Mode, the Cybereason Defense Platform also detects the code injection into “notepad.exe” and prevents it from executing further:
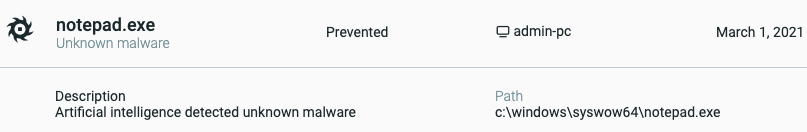
Conclusion
Social engineering via phishing has been, and continues to be, the preferred infection method among cyber criminals and nation-state threat actors alike. In order to succeed, the threat actor must choose an interesting theme that is likely to lure its victim into opening the weaponized document or link.
In the campaign, we have demonstrated how cybercriminals are leveraging the US tax season to infect American taxpayers with the Remcos and NetWire remote access trojans, granting the malware operators full access and control over the victims’ machines. The sensitive information collected from the victims can be used by the attackers to carry out financial fraud or can be traded in the underground communities.
Cybereason also noticed efforts by the threat actor designed the campaign to stay under the radar, using various techniques such as steganography, storing payloads on legitimate cloud-based services, and exploiting DLL sideloading against a legitimate software.
Looking for the IOCs? Click on the chatbot displayed in lower-right of your screen.
MITRE ATT&CK BREAKDOWN







 Malicious documents submitted to VirusTotal
Malicious documents submitted to VirusTotal



.png?width=512&name=unnamed%20(1).png) The loader’s exported methods
The loader’s exported methods









